What is an osteopathic clinical trial?
An osteopathic clinical trial is a research study designed to understand the safety, effectiveness, and/or biological mechanisms of osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM), or more generally osteopathic principles and practice (OP&P). As with other clinical trials, these studies will test an intervention to see how well it works and/or how safe the intervention is in a group of individuals who volunteer to be a part of these studies (clinical trial participants).
What types of interventions are tested?
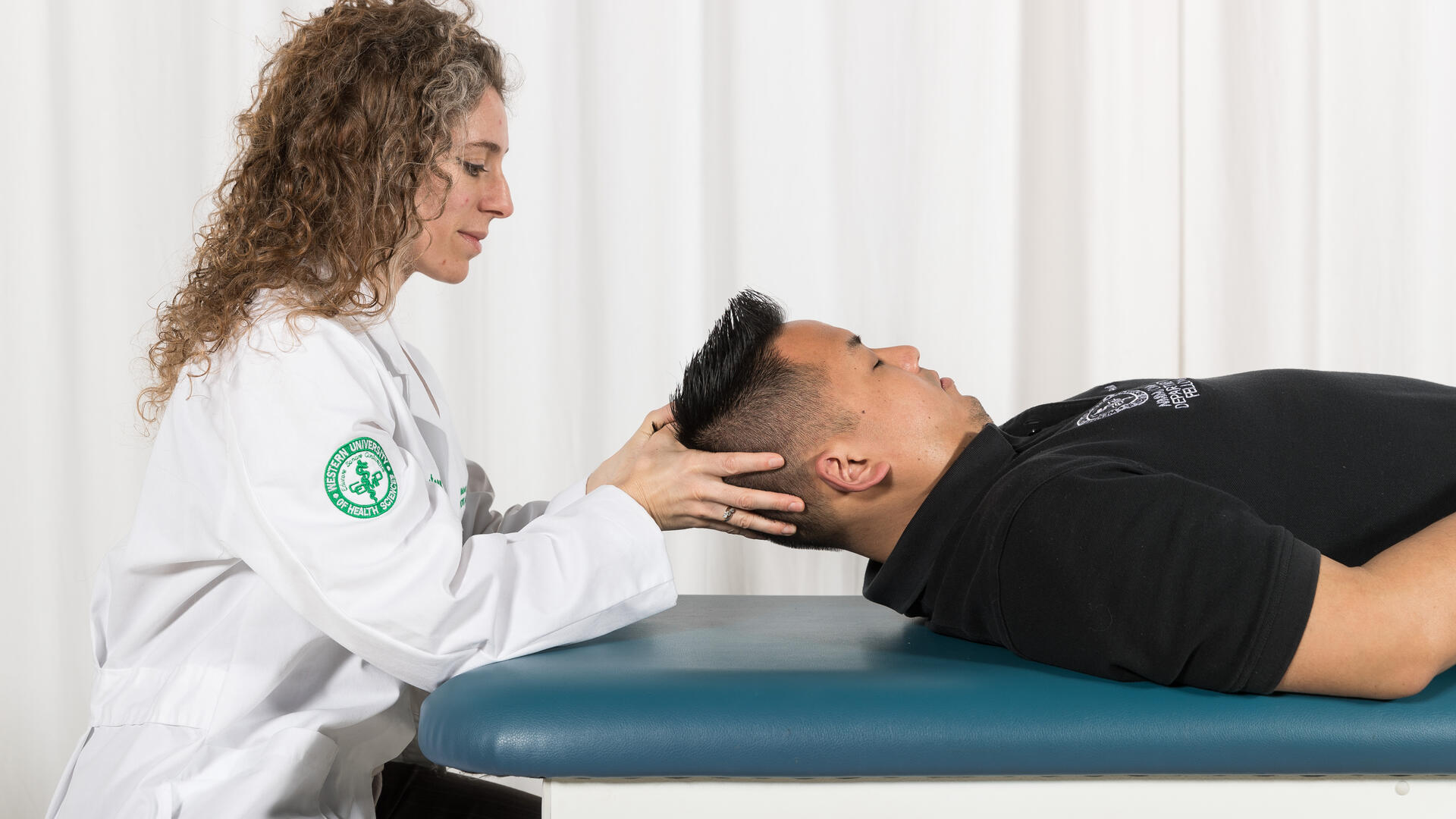
The main intervention test in osteopathic clinical trials is usually OMT, but it can also include other aspects of osteopathic care including holistic management of health issues, preventative measures, and lifestyle modifications. OMT typically consists of hands-on, manual therapy including stretching, pressure, and resistance, that is performed by Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (DOs) to diagnose, treat, and prevent illness by addressing somatic dysfunctions in the body. Somatic dysfunctions are impairments or imbalances in the body's structure or function that lead to all kinds of health issues.
What are the study designs used in these trials?
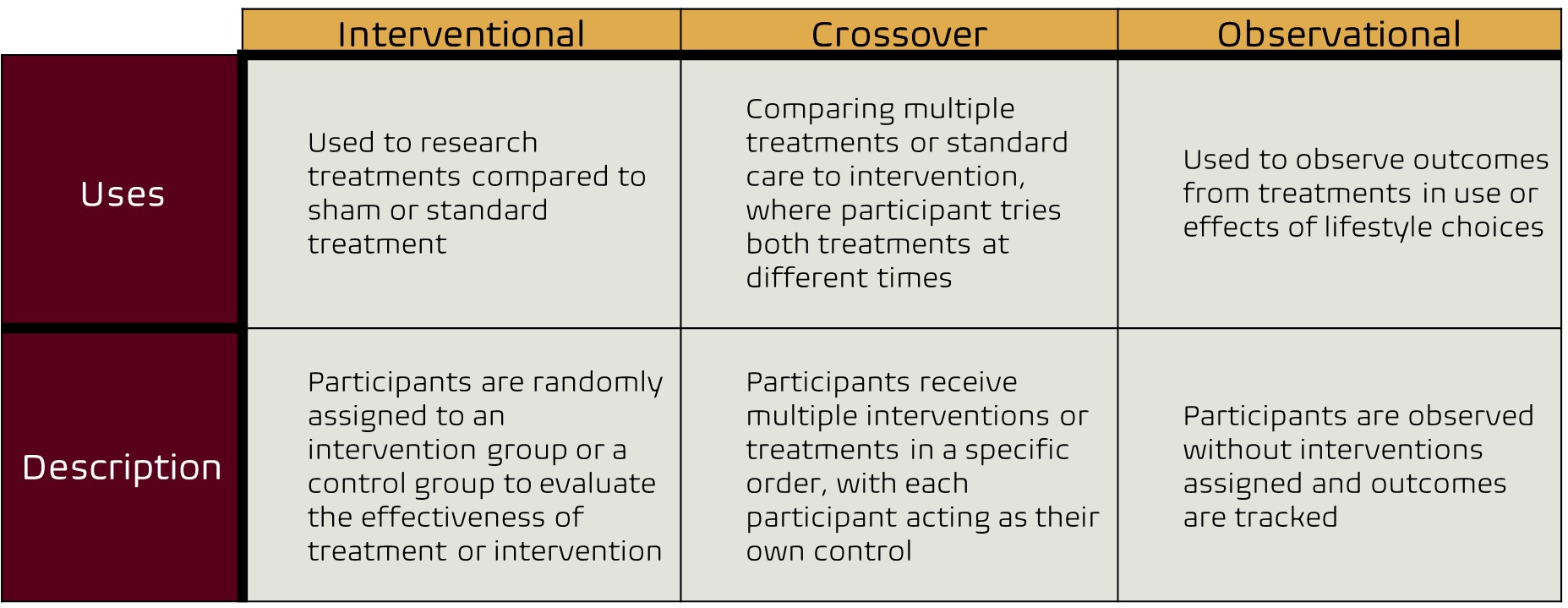
What are randomized controlled trials (RCTs)?
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) - A scientific study used to investigate the effectiveness of treatment or intervention by assigning participants to random groups. One group receives some kind of intervention (intervention group), while the other randomized group receives sham treatment or standard treatment (control group). This usually involves blinding, where either the participant, researchers, or both do not know which group participants are randomly assigned. Randomizing the participants allows researchers to lessen the chance of bias or personal beliefs influencing outcomes, so they can be sure that the differences seen between groups are due to the intervention or treatment.